Utilise Multiprocessing to Improve Python Kafka Transformer Throughput
What I mean by transformer is program that consume event from kafka, “transform” the event, than produce it back to kafka. Transformer is not a common way to say this operation.
Prepare The Kafka Broker
Lets start with prepare the kafka broker. Here I will use Redpanda. You can learn more about Redpanda in the Redpanda website at https://www.redpanda.com/. In simple terms, Redpanda is message broker that using Kafka protocol as interface. Using Kafka protocol as interface means you can use any existing kafka client or library without changing anything (except connection details of course) and in theory it should be working as expected. I already prepare docker-compose.yaml file for easy deployment.
Make sure
gitanddocker-composeis installed.
git clone https://github.com/rochimfn/compose-collection.git
cd compose-collection/redpanda
docker-compose up -d # or docker compose up -d
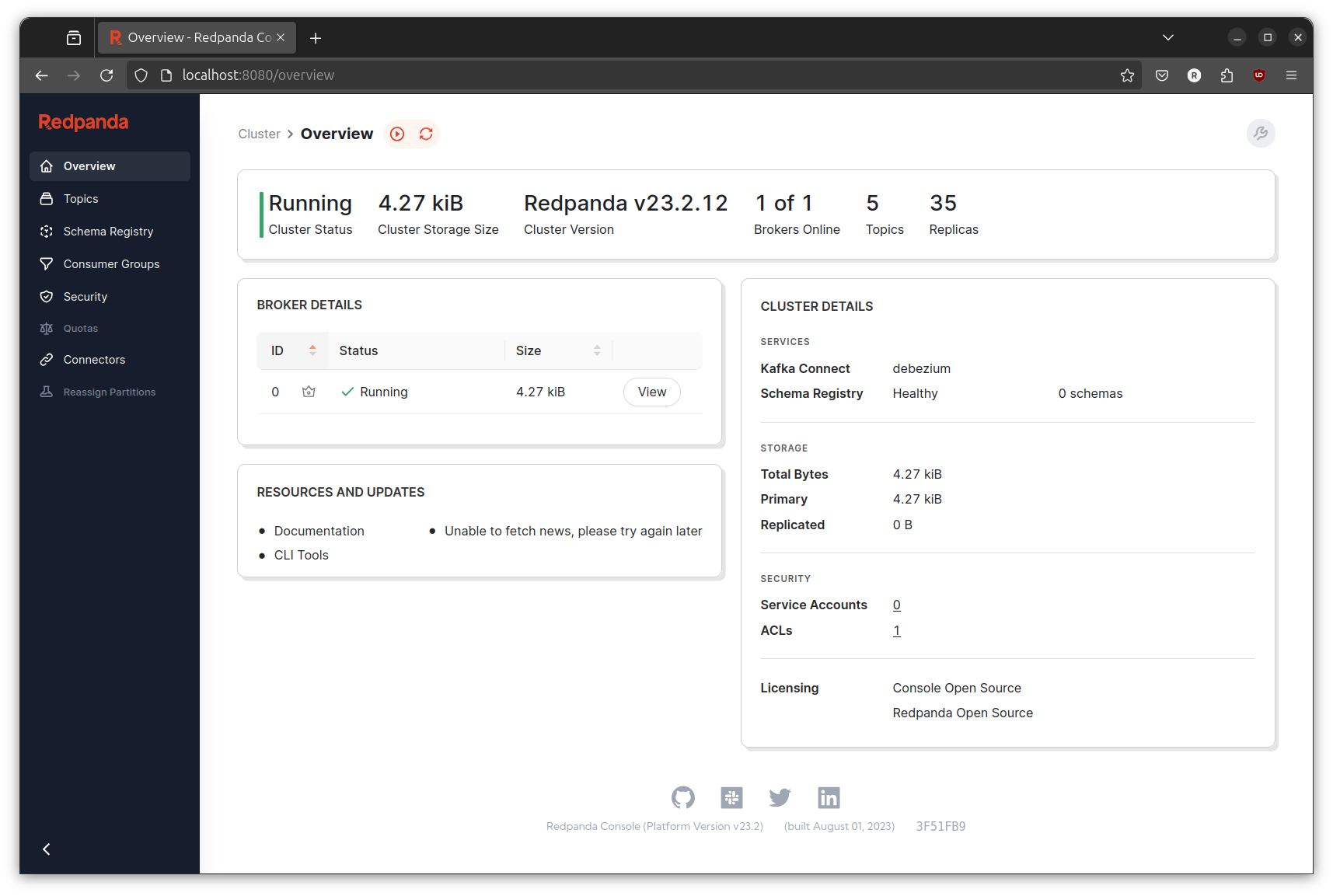
Go to http://localhost:8080/overview to check if redpanda successfully running. You should see below page.
Prepare The Event Generator
I have created simple event generator using golang. The generator will produce event in json format into name_stream topic. The event contain two field first_name and last_name.
Example event:
{"first_name":"Bonita","last_name":"Kautzer"}
To install the generator, you will need git and go installed. Follow the golang documentation at https://go.dev/doc/install to learn how to install golang to your OS.
git clone https://github.com/rochimfn/go-mock-name-kafka.git
cd go-mock-name-kafka
go run main.go
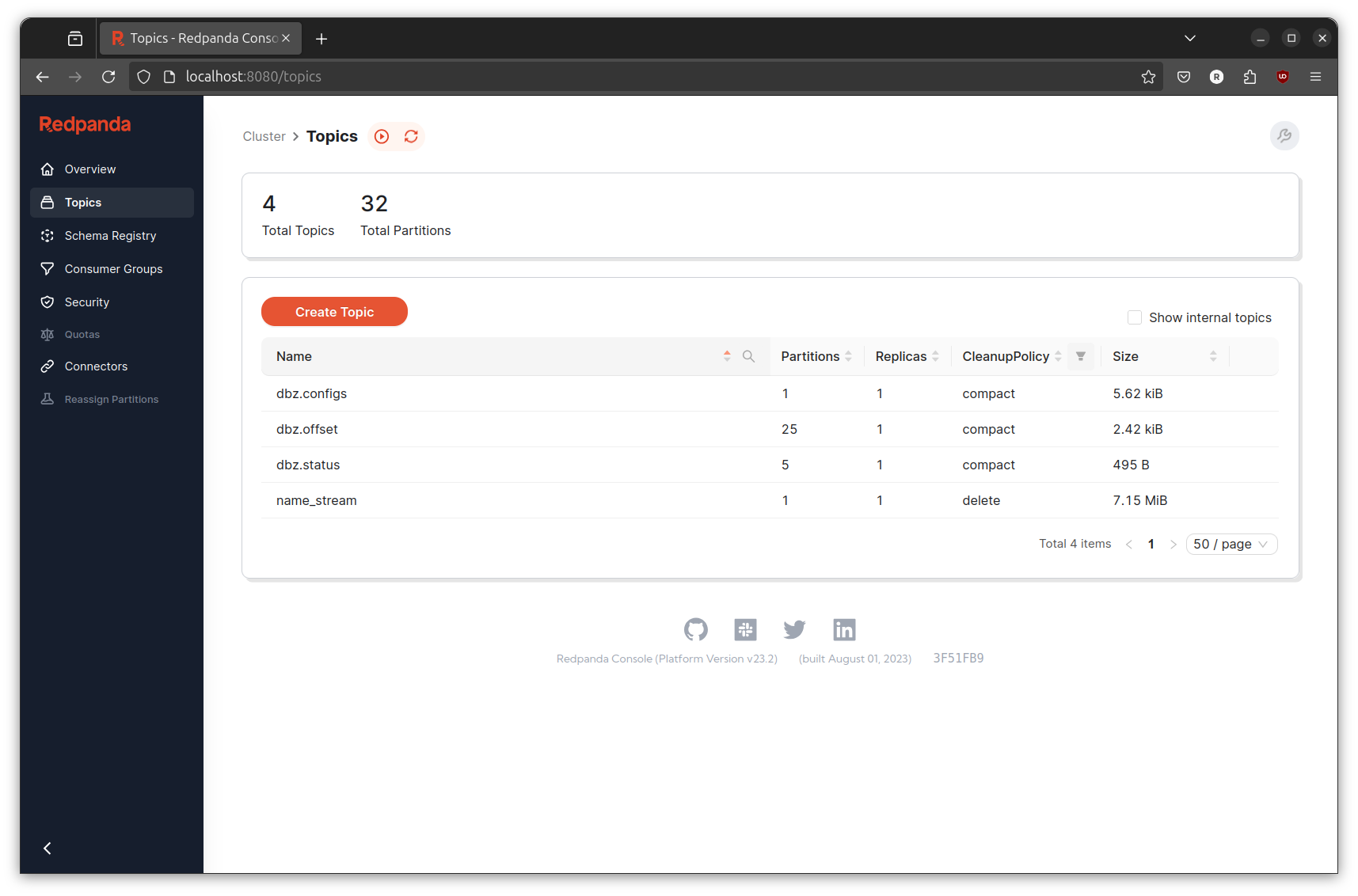
Check Topics page on Redpanda console and you will find new topic is created. Click on the new generated topic and you will see the event is continuously created when the event generator is running.
Hit ctrl+c on your keyboard to stop the event generator.
You may need to change connection details at line 15-19. The event generator is built using golang version 1.23.4.
Built Python Transformer: The Serial Way
Before going into multiprocessing, lets start with implementing the python transformer in serial way since it is the most simple one. Serial means the transformer will “do” the process one-by-one without any concurrency.
The transformer will have simple job:
- consume the event,
- generate the md5 hash of the event,
- add the generated md5 hash into the event, and
- produce the event into the different topic
I will be using python version 3.12 with library confluent-kafka. The confluent-kafka may need librdkafka to be installed in the OS. In Ubuntu, the librdkafka can be installed using the below command:
sudo apt install librdkafka-dev
Also in Ubuntu, the venv module may not be installed automatically. You may use below command to install:
sudo apt install python3.12-venv
Create the directory and virtual environment for the transformer:
mkdir python-kafka-serial-transformer
cd python-kafka-serial-transformer
python3 -m venv venv
. venv/bin/activate
Install the confluent-kafka library:
pip install confluent-kafka
Create script.py file with below content:
from confluent_kafka import Consumer, Producer
from confluent_kafka.error import KafkaError, KafkaException
import hashlib
import json
import sys
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
topic = 'name_stream'
destination_topic = 'name_stream_serial_transformed'
broker = "localhost:19092"
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'group.id': "consumer_python_serial"}
def ack(err, msg):
if err is not None:
logging.info("Failed to deliver message: %s: %s" % (str(msg), str(err)))
else:
logging.info("Successfully produced message {} into {}[{}]@{} ".format(str(msg.value()), str(msg.topic()), str(msg.partition()), str(msg.offset())))
def consume_loop(consumer, broker, topics, destination):
logging.info('prepare producer')
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker}
producer = Producer(conf)
logging.info('start consume')
try:
consumer.subscribe(topics)
while True:
logging.info('pollling')
# consuming
msg = consumer.poll(timeout=1.0)
if msg is None: continue
if msg.error():
if msg.error().code() == KafkaError._PARTITION_EOF:
sys.stderr.write('%% %s [%d] reached end at offset %d\n' %
(msg.topic(), msg.partition(), msg.offset()))
elif msg.error():
raise KafkaException(msg.error())
else:
# tranformation
key = msg.key()
value = json.loads(msg.value())
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(msg.value()).hexdigest()
# producer
producer.produce(destination, key=key, value=json.dumps(value), callback=ack)
producer.poll(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logging.info('receive interrupt')
finally:
consumer.close()
def main():
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consume_loop(consumer=consumer, broker=broker, topics=[topic], destination=destination_topic)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
When the script.py is executed it will do the import defined at the top of the file:
from confluent_kafka import Consumer, Producer
from confluent_kafka.error import KafkaError, KafkaException
import hashlib
import json
import sys
import logging
Then, it will setup the logging and defined the variable that will be used to connect to redpanda:
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
topic = 'name_stream'
destination_topic = 'name_stream_serial_transformed'
broker = "localhost:19092"
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'group.id': "consumer_python_serial"}
Then the main function is executed. The main function consist of consumer object/connection definition and call to consume_loop function:
def main():
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consume_loop(consumer=consumer, broker=broker, topics=[topic], destination=destination_topic)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
The consume_loop function (as the name suggest) contains the main process of the transformer. The consume_loop will continuously consume event from the broker than processed it until it received KeyboardInterrupt (ctrl+c) or another type of Exception.
def ack(err, msg):
if err is not None:
logging.info("Failed to deliver message: %s: %s" % (str(msg), str(err)))
else:
logging.info("Successfully produced message {} into {}[{}]@{} ".format(str(msg.value()), str(msg.topic()), str(msg.partition()), str(msg.offset())))
def consume_loop(consumer, broker, topics, destination):
logging.info('prepare producer')
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker}
producer = Producer(conf)
logging.info('start consume')
try:
consumer.subscribe(topics)
while True:
logging.info('pollling')
# consuming
msg = consumer.poll(timeout=1.0)
if msg is None: continue
if msg.error():
if msg.error().code() == KafkaError._PARTITION_EOF:
sys.stderr.write('%% %s [%d] reached end at offset %d\n' %
(msg.topic(), msg.partition(), msg.offset()))
elif msg.error():
raise KafkaException(msg.error())
else:
# tranformation
key = msg.key()
value = json.loads(msg.value())
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(msg.value()).hexdigest()
# producer
producer.produce(destination, key=key, value=json.dumps(value), callback=ack)
producer.poll(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logging.info('receive interrupt')
finally:
consumer.close()
Run the event generator so the topics will be populated:
cd go-mock-name-kafka
go run main.go
Then run the python transformer:
cd python-kafka-serial-transformer
. venv/bin/activate
python script.py
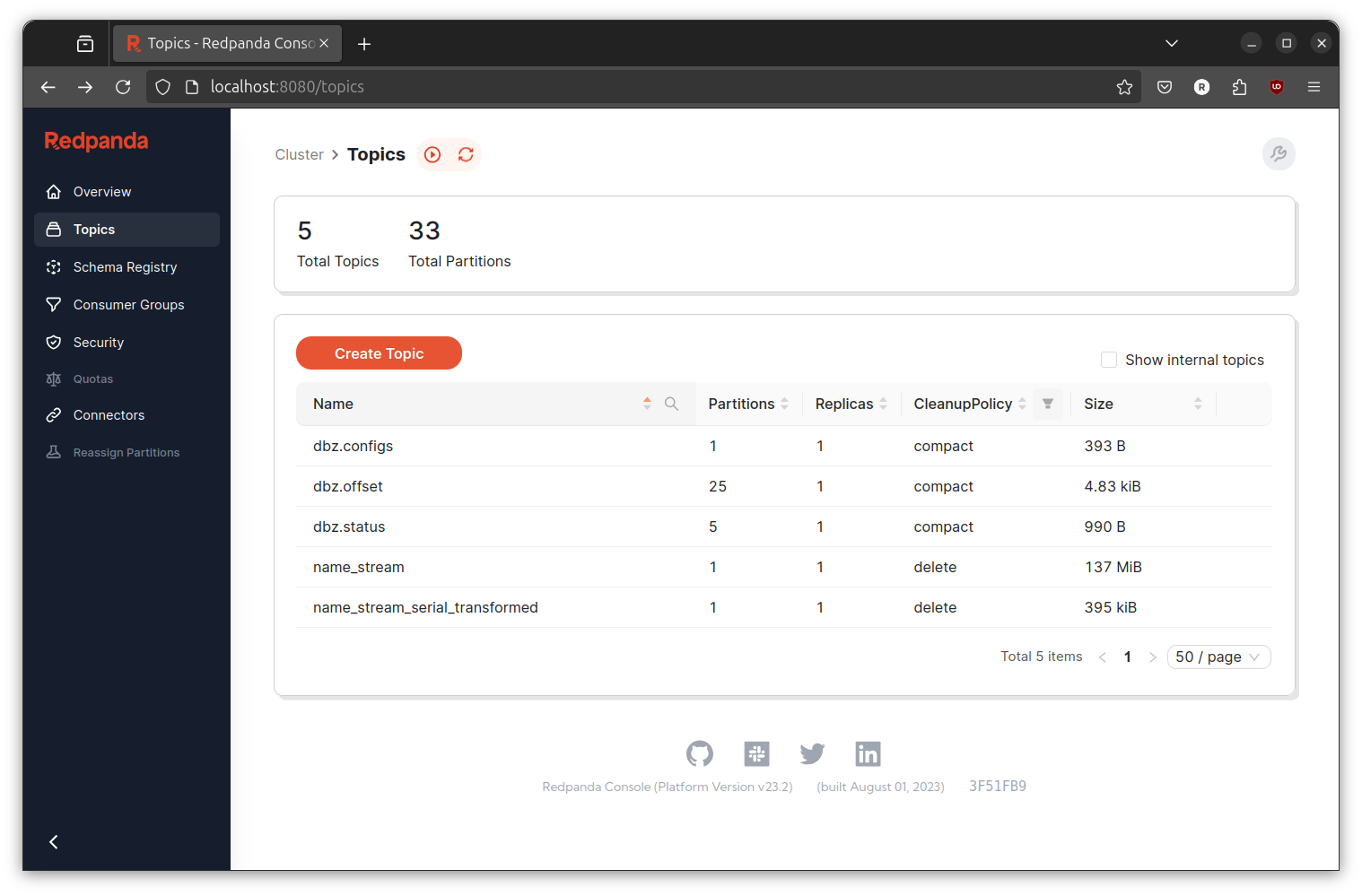
Check on the Redpanda console and you will find new topic with the name name_stream_serial_transformed. You can click on it and it will show you the event result.
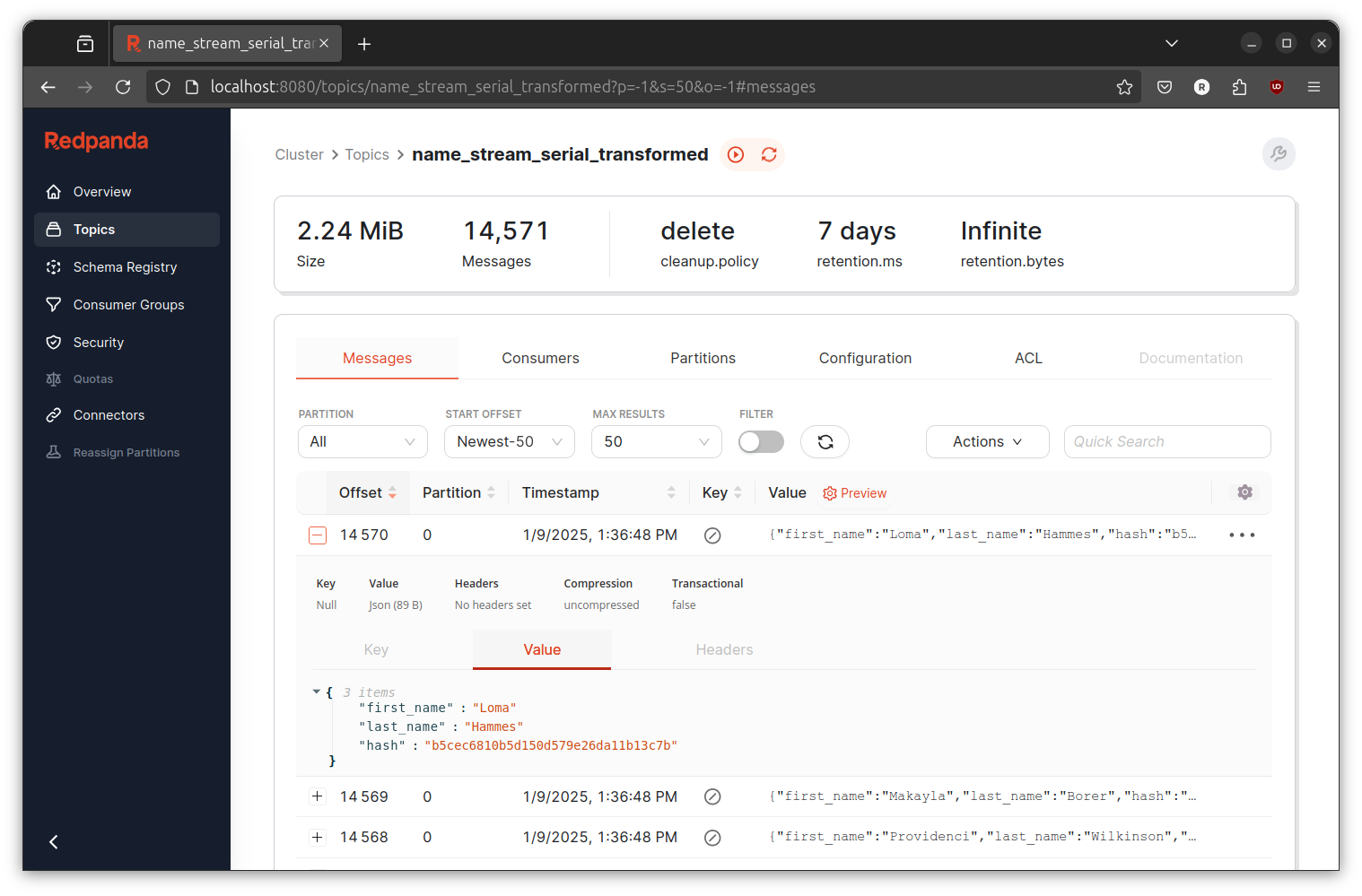
Back to topics page and click on name_stream topic. Then, click on Consumers to view the current active consumer and the number of lag. Lag is the number of event that is not yet consumed by the consumer. We can use this number to determine wether our transformer have good enough processing rate or not.
While both event generator and transformer is running, write the current number of lag. After 30 second, refresh the page and compare the number of lag. In my machine with Ryzen 5 4500u processor, 16G memory, M.2 NVME SSD running Ubuntu 24.04 the number is rapidly increasing showing that the event generator produce rate is higher than our transformer process rate. This situation is called backpressure.
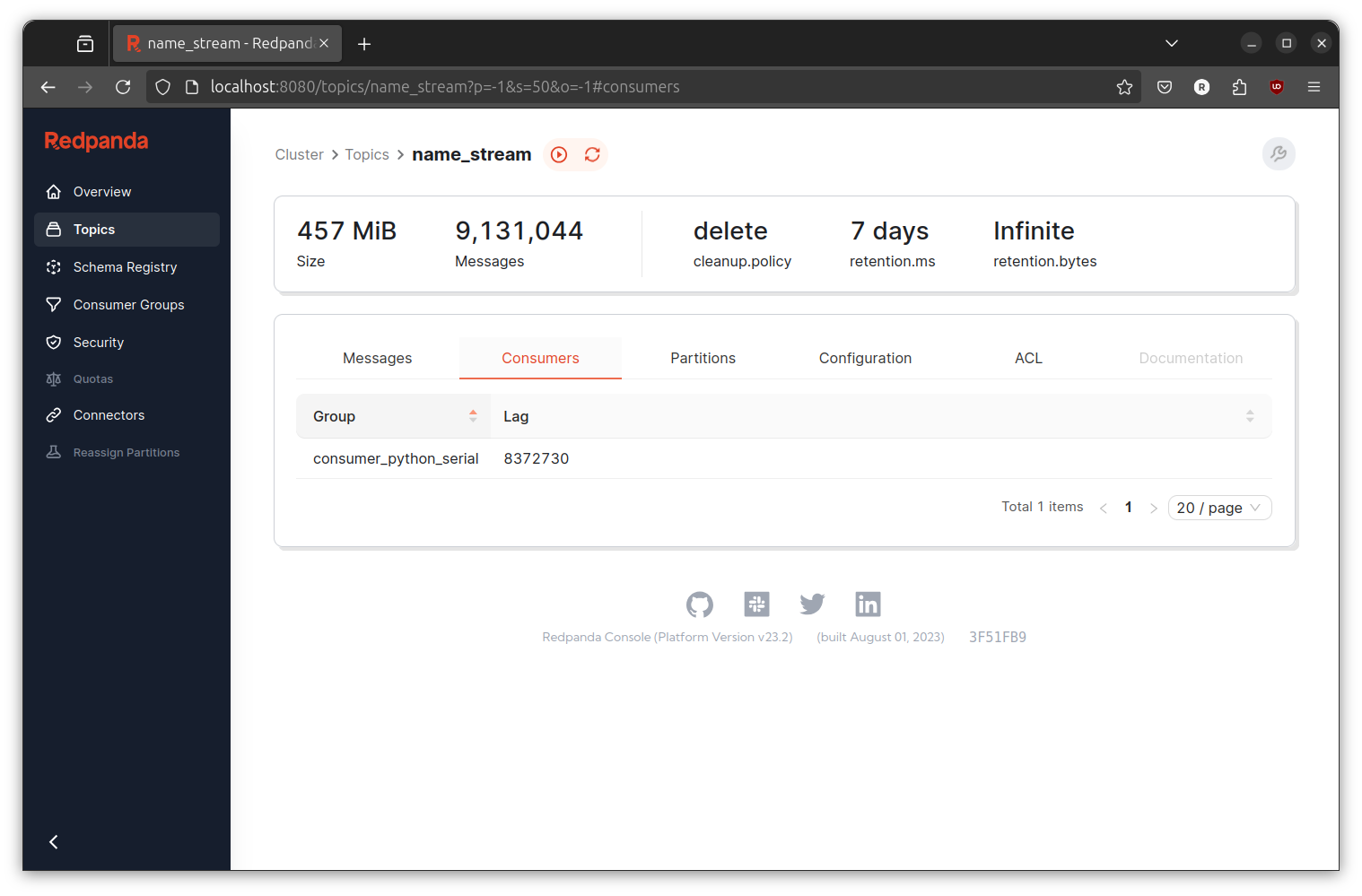
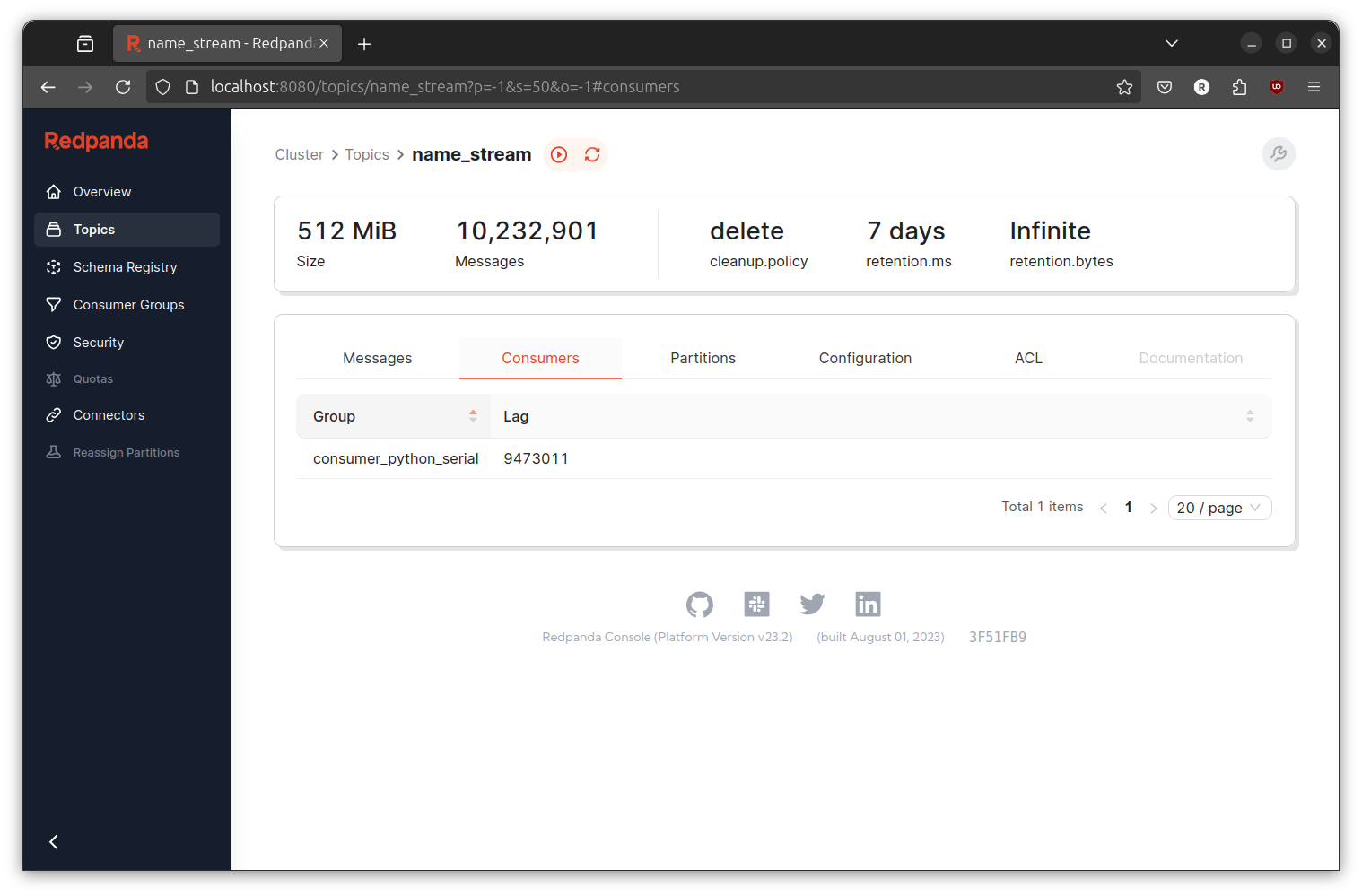
In real world, backpressure is not always a problem since the system may have some quiet time while the system is not actively being use by the customer and the produce rate is lower. But, if we assume the worse scenario where both producer (event generator) and consumer (transformer) is always running at full capacity, the event may encounter kafka retention before consumed by the consumer (say hello to data lost).
There are at least three way to avoid backpressure. First, is to increase the number of topic partition and the consumer. Second, is to improve the troughput of the consumer. Last but not least, let the data lost.
Built Parallel Python Transformer: The “New to Multiprocessing” Way
I don’t know about you but everytime I learn about multiprocessing in python, every code I encounter is look like below:
from multiprocessing import Pool
import os
def f(x):
print(x)
with Pool(os.cpu_count()) as p:
p.map(f, [1, 2, 3])
Lets follow the pattern. Open new terminal and create another python project:
mkdir python-kafka-multiprocessing-transformer-1
cd python-kafka-multiprocessing-transformer-1
python3 -m venv venv
. venv/bin/activate
pip install confluent-kafka
Copy script.py from serial implementation and lets make some adjustment. First, the map function of multiprocessing.Pool want input in list shape. Fortunately confluent-kafka already provide convenient function consume that will automatically get multiple message from kafka then wrap it as list. You can learn more about this function here.
num_messages = os.cpu_count()*12
while True:
# consuming
logging.info('pollling')
msgs = consumer.consume(num_messages=num_messages, timeout=30.0)
if msgs is None: continue
elif len(msgs) == 0: continue
Next, python need the input to be “pickleable” so it can be passed to another process. Unfotunately, the Message type is not pickleable so we will need to process it first.
def map_messages(msgs):
mapped_msgs = []
for msg in msgs:
if msg is not None and not msg.error(): mapped_msgs.append({"key": msg.key(), "value": msg.value()})
elif msg is None: continue
else: logging.error(msg.error())
return mapped_msgs
The code part that we need to paralellize must be converted as separate function. Here I will only paralellize the hashing part.
def process(msg):
# tranformation
key = msg['key']
value = json.loads(msg['value'])
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(msg['value']).hexdigest()
# producer
return (key, value)
The produce part can also be paralellize but then the connection handling will be pain since the connection should be passed to every created process. Meaning, the connection should be “thread safe” and or pickleable. We can also create (and destroy) connection for every created process but then it will be resources heavy and potentially not gain any speed up. Here is the final code:
from confluent_kafka import Consumer, Producer
from confluent_kafka.error import KafkaError, KafkaException
import hashlib
import json
import sys
import logging
import os
import multiprocessing as mp
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
topic = 'name_stream'
destination_topic = 'name_stream_parallel1_transformed'
broker = "localhost:19092"
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'group.id': "consumer_python_parallel1"}
def ack(err, msg):
if err is not None:
logging.info("Failed to deliver message: %s: %s" % (str(msg), str(err)))
else:
logging.info("Successfully produced message {} into {}[{}]@{} ".format(str(msg.value()), str(msg.topic()), str(msg.partition()), str(msg.offset())))
def process(msg):
# tranformation
key = msg['key']
value = json.loads(msg['value'])
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(msg['value']).hexdigest()
# producer
return (key, value)
def map_messages(msgs):
mapped_msgs = []
for msg in msgs:
if msg is not None and not msg.error(): mapped_msgs.append({"key": msg.key(), "value": msg.value()})
elif msg is None: continue
else: logging.error(msg.error())
return mapped_msgs
def consume_loop(consumer, broker, topics, destination):
logging.info('prepare producer')
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker}
producer = Producer(conf)
p = mp.Pool(os.cpu_count())
logging.info('start consume')
try:
consumer.subscribe(topics)
num_messages = os.cpu_count()*12
while True:
# consuming
logging.info('pollling')
msgs = consumer.consume(num_messages=num_messages, timeout=30.0)
if msgs is None: continue
elif len(msgs) == 0: continue
transformed_msgs = p.map(process, map_messages(msgs))
for msg in transformed_msgs:
producer.produce(destination, key=msg[0], value=json.dumps(msg[1]), callback=ack)
producer.flush()
except KeyboardInterrupt:
logging.info('receive interrupt')
finally:
consumer.close()
p.close()
def main():
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consume_loop(consumer=consumer, broker=broker, topics=[topic], destination=destination_topic)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Delete all the left over topic then run the event generator and the newly created transformer. Observe the console and consumer lag.
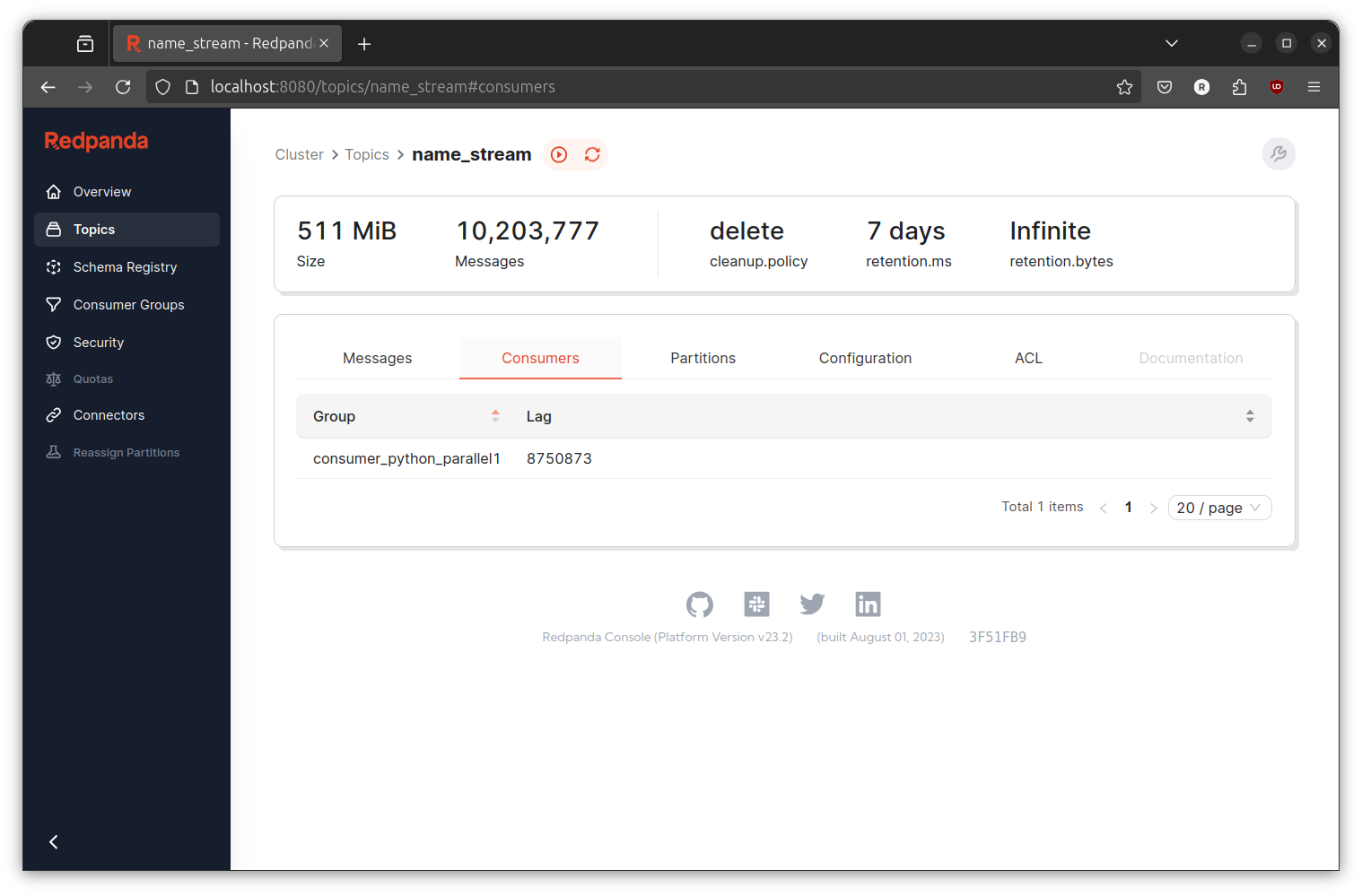
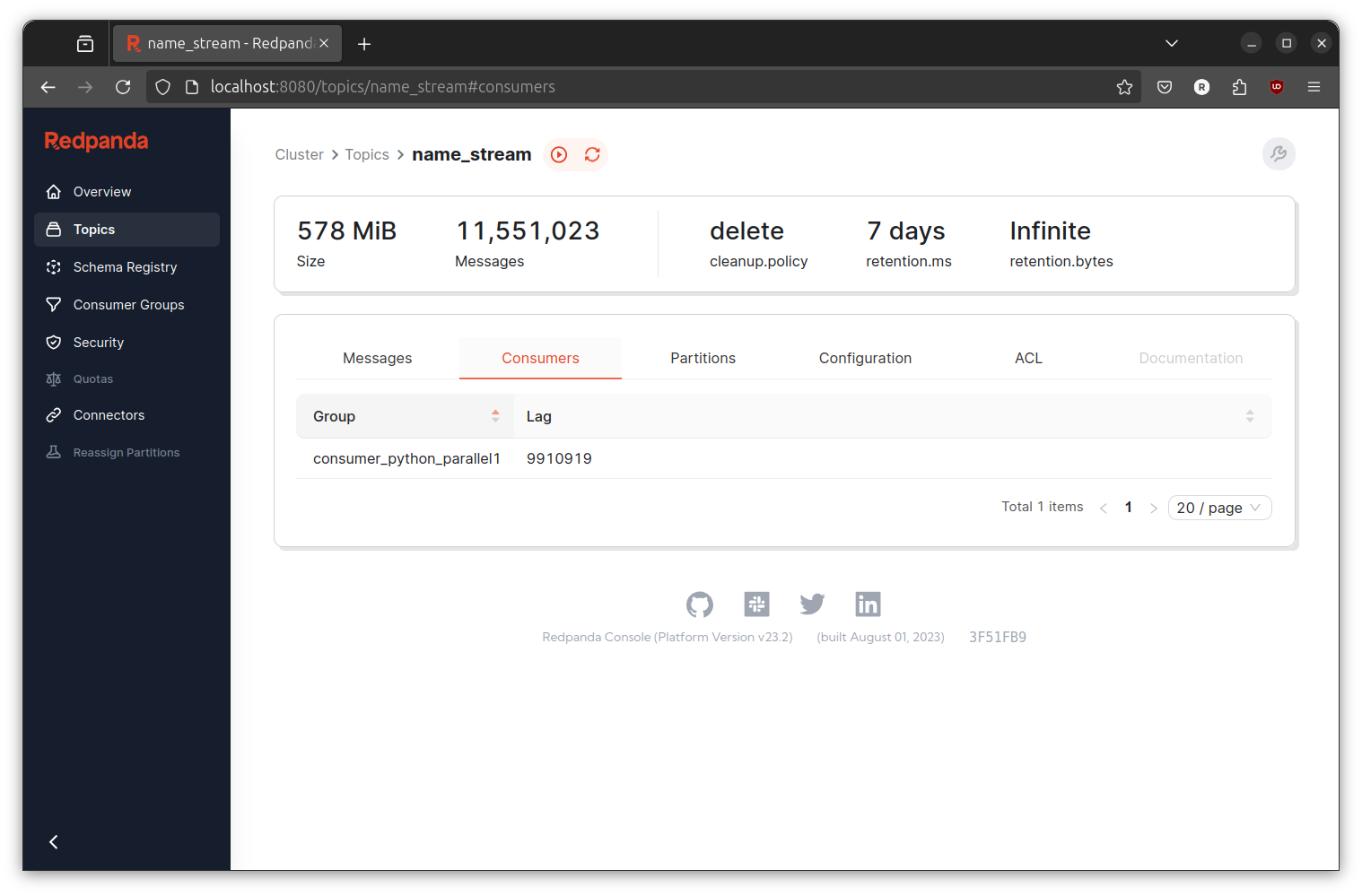
Unfortunately, in my machine the number keep increasing like the serial version.
- Why is this happening? I don’t know,
- Are our script is really running in parallel? Looking at the system monitor I can see the script is actively creating subprocess,
- Are we paralellize the wrong part of the code? Maybe yes maybe no, we need to measure every part of the code to actually find the slowest part,
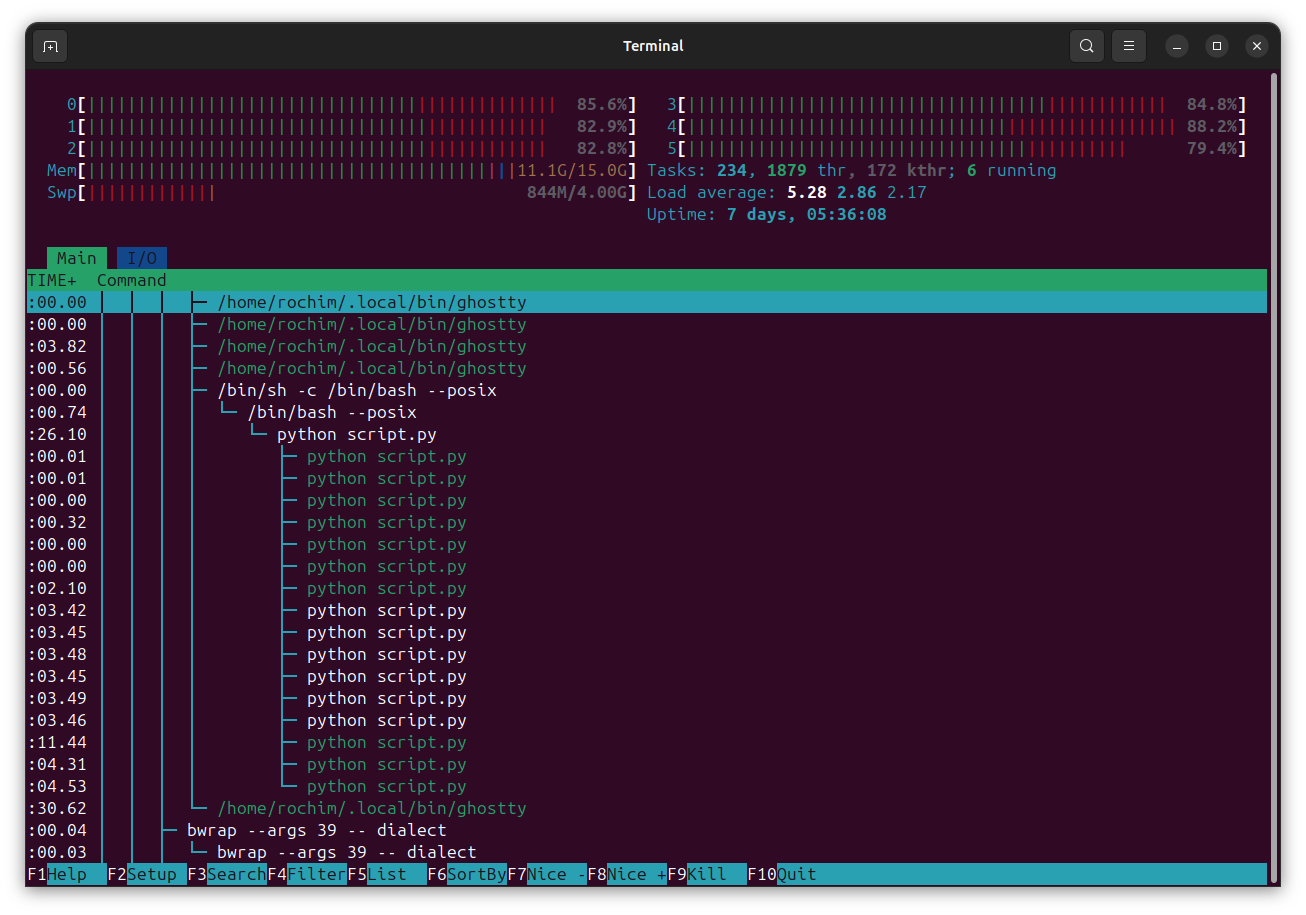
What is certain to me is (by looking at the code) there are a lot of waiting in the code. When the consume part is running, the (paralell) hash generation and the produce part is waiting. When the hash generation is running, the consume and produce part is waiting. Same case when the produce part is running, other part of code is waiting. Lets try again but now we will make every part independent.
Built Parallel Python Transformer: The Pipelining Way
How to make every part of the code independent? Let me introduce you to multiprocessing.Queue. multiprocessing.Queue enable subprocess created with multiprocessing module to communicate to with each other. Of course as the name suggest, we are limited to only use queue data structure to communicate, meaning the communication may only flow in one direction and in ordered manner. But it is more than enough. If you want to learn more please read the documentation here.
In the meantime lets create new python project. Open new terminal and run below command:
mkdir python-kafka-multiprocessing-transformer-2
cd python-kafka-multiprocessing-transformer-2
python3 -m venv venv
. venv/bin/activate
pip install confluent-kafka
Maybe you already notice this, when you hit ctrl+c on the last script, sometimes the script it is not exiting. This is because we don’t correctly handle the KeybordInterrupt in multiprocess environment. In this version, lets correctly handle this. Lets create “switch” that will react to KeyboardInterrupt or any other interrupt.
class Switch():
is_active = True
def __init__(self):
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, self.turn_off)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, self.turn_off)
def turn_off(self, *_):
self.is_active = False
The switch will be used by the first stage of the pipeline, the consumer part. When the switch is turned off by interrupt or terminate signal, the consumer will stop consuming the event from kafka and propagate the interrupt signal to the next part of the pipeline.
Even after you implement the switch, the script may not exit immediately when you hit
ctrl+c. This is because the script need to process all the pending event inside the queue before the script can exit.
Implement the consumer part into separated function. Since the consumer is consuming the event directly from kafka we only need one queue, queue to put message.
def consumer(q, switch):
logging.info("consumer started")
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'group.id': group_id}
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consumer.subscribe([topic])
while switch.is_active:
msg = consumer.poll(1)
if msg is None: continue
if msg.error():
if msg.error().code() == KafkaError._PARTITION_EOF:
sys.stderr.write('%% %s [%d] reached end at offset %d\n' % (msg.topic(), msg.partition(), msg.offset()))
elif msg.error(): logging.error(msg.error())
else:
q.put((msg.key(), msg.value()))
logging.info("consumer receiving signal")
consumer.close()
q.put(signal.SIGINT)
When the switch is still active, the consumer will consume event from kafka one at a time then put it to the queue. When the switch is not active the consumer loop will stop and close the consumer connection then propagate interrupt signal.
Next implement the hashing part into another separated function. The hasher will need two queue. The first one is input queue, this is the same queue where the consumer is puting message into. The second one is output queue, this is the queue where the hasher will put the hasher result.
def hasher(consumer_q, producer_q):
logging.info('hasher started')
while True:
# tranformation
logging.info("hasher poll")
item = consumer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("hasher receiving signal")
producer_q.put(signal.SIGINT)
return
key = item[0]
value = json.loads(item[1])
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(item[1]).hexdigest()
producer_q.put((key, value))
The hasher will consume the event coming from consumer and process the hashes unless the event is interrupt signal.
Next implement the producer part into separated function. The producer will consume the result from hasher trough queue then produced it to kafka.
def ack(err, msg):
if err is not None:
logging.info("Failed to deliver message: %s: %s" % (str(msg), str(err)))
else:
logging.info("Successfully produced message {} into {}[{}]@{} ".format(str(msg.value()), str(msg.topic()), str(msg.partition()), str(msg.offset())))
def producer(producer_q):
logging.info("producer started")
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'queue.buffering.max.messages': queue_limit}
producer = Producer(conf)
while True:
logging.info("producer poll")
item = producer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("producer receiving signal")
unflushed = producer.flush()
logging.info(f"unflushed: {unflushed}")
break
# producer
try:
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
except BufferError:
producer.flush()
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
producer.flush()
I add new config queue.buffering.max.messages to producer config. This configuration is responsible to set the number of queue slot inside the internal of confluent-kafka producer. You can learn more about the configuration here. The default value is low, thats way here I will increased it trough queue_limit variable. Also here I add exception handler for BufferError. The exception BufferError is triggered when we try to produce (aka queueing) new event into full internal confluent-kafka producer queue. When it happened, simply flush all queue and retry produce.
Lastly, lets assamble the pipeline with main function.
def main():
s = Switch()
consumer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
producer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
consumer_process = mp.Process(target=consumer, args=(consumer_q,s,))
hasher_process = mp.Process(target=hasher, args=(consumer_q, producer_q,))
producer_process = mp.Process(target=producer, args=(producer_q,))
consumer_process.start()
hasher_process.start()
producer_process.start()
consumer_process.join()
hasher_process.join()
producer_process.join()
consumer_process.close()
hasher_process.close()
producer_process.close()
logging.info('all done')
The main function is responsible to prepare the switch and queue needed by the pipeline. The queue limit must be set to queue to create necessary backpressure and to limit the number event inside the pipeline (effectively limit the memory usage too). Then the main function will start the individual process for each function.
Here is the full code:
from confluent_kafka import Consumer, Producer
from confluent_kafka.error import KafkaError
import hashlib
import json
import sys
import logging
import multiprocessing as mp
import signal
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
topic = 'name_stream'
destination_topic = 'name_stream_parallel2_transformed'
group_id = "consumer_python_parallel2"
broker = "localhost:19092"
queue_limit = 1000 * 1000
class Switch():
is_active = True
def __init__(self):
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, self.turn_off)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, self.turn_off)
def turn_off(self, *_):
self.is_active = False
def consumer(q, switch):
logging.info("consumer started")
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'group.id': group_id}
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consumer.subscribe([topic])
while switch.is_active:
msg = consumer.poll(1)
if msg is None: continue
if msg.error():
if msg.error().code() == KafkaError._PARTITION_EOF:
sys.stderr.write('%% %s [%d] reached end at offset %d\n' % (msg.topic(), msg.partition(), msg.offset()))
elif msg.error(): logging.error(msg.error())
else:
q.put((msg.key(), msg.value()))
logging.info("consumer receiving signal")
consumer.close()
q.put(signal.SIGINT)
def hasher(consumer_q, producer_q):
logging.info('hasher started')
while True:
# tranformation
logging.info("hasher poll")
item = consumer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("hasher receiving signal")
producer_q.put(signal.SIGINT)
return
key = item[0]
value = json.loads(item[1])
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(item[1]).hexdigest()
producer_q.put((key, value))
def ack(err, msg):
if err is not None:
logging.info("Failed to deliver message: %s: %s" % (str(msg), str(err)))
else:
logging.info("Successfully produced message {} into {}[{}]@{} ".format(str(msg.value()), str(msg.topic()), str(msg.partition()), str(msg.offset())))
def producer(producer_q):
logging.info("producer started")
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'queue.buffering.max.messages': queue_limit}
producer = Producer(conf)
while True:
logging.info("producer poll")
item = producer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("producer receiving signal")
unflushed = producer.flush()
logging.info(f"unflushed: {unflushed}")
break
# producer
try:
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
except BufferError:
producer.flush()
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
producer.flush()
def main():
s = Switch()
consumer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
producer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
consumer_process = mp.Process(target=consumer, args=(consumer_q,s,))
hasher_process = mp.Process(target=hasher, args=(consumer_q, producer_q,))
producer_process = mp.Process(target=producer, args=(producer_q,))
consumer_process.start()
hasher_process.start()
producer_process.start()
consumer_process.join()
hasher_process.join()
producer_process.join()
consumer_process.close()
hasher_process.close()
producer_process.close()
logging.info('all done')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Now we are ready to run the event generator and the new transformer. But before that, remove the left over topics from last run.
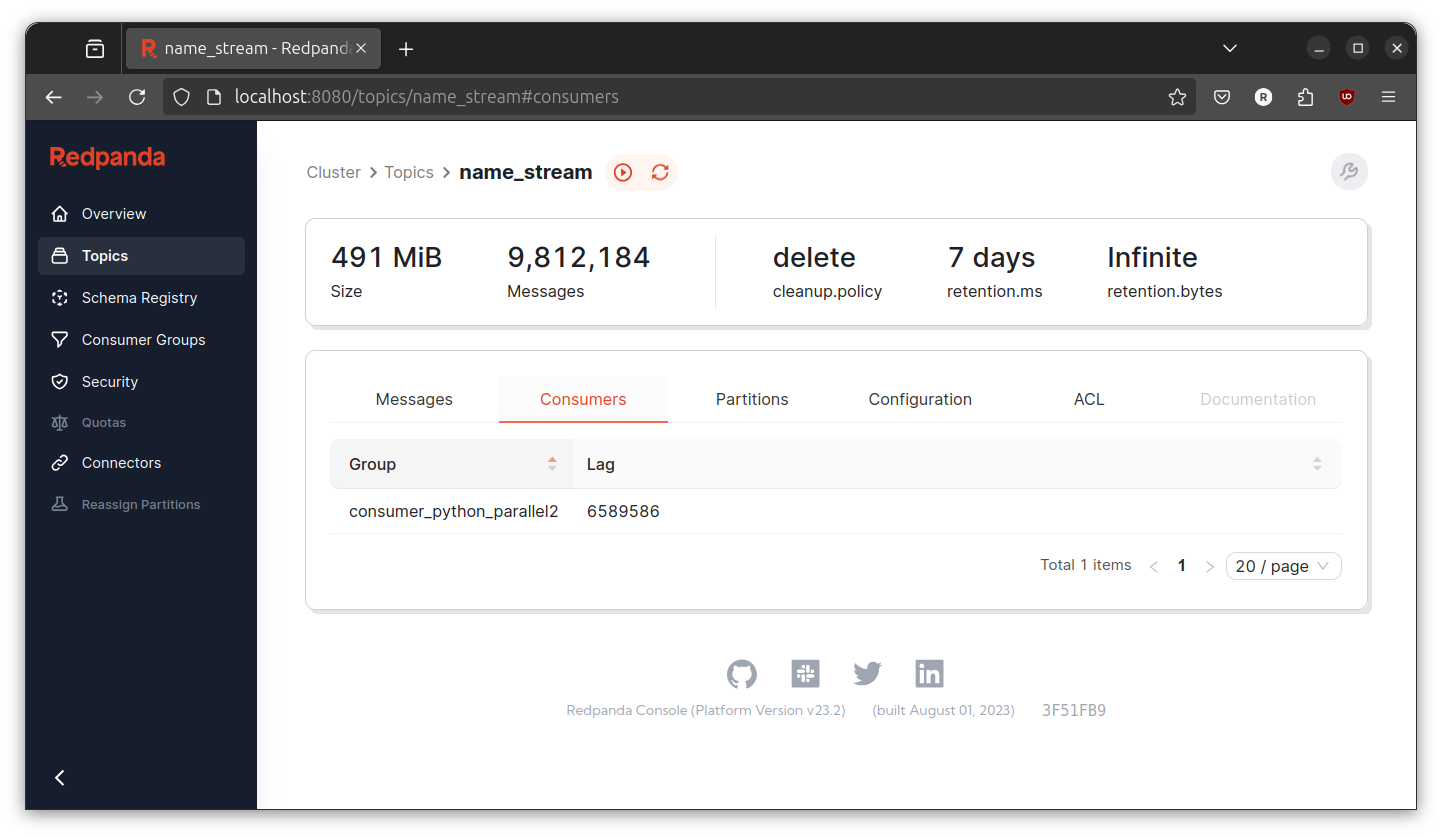
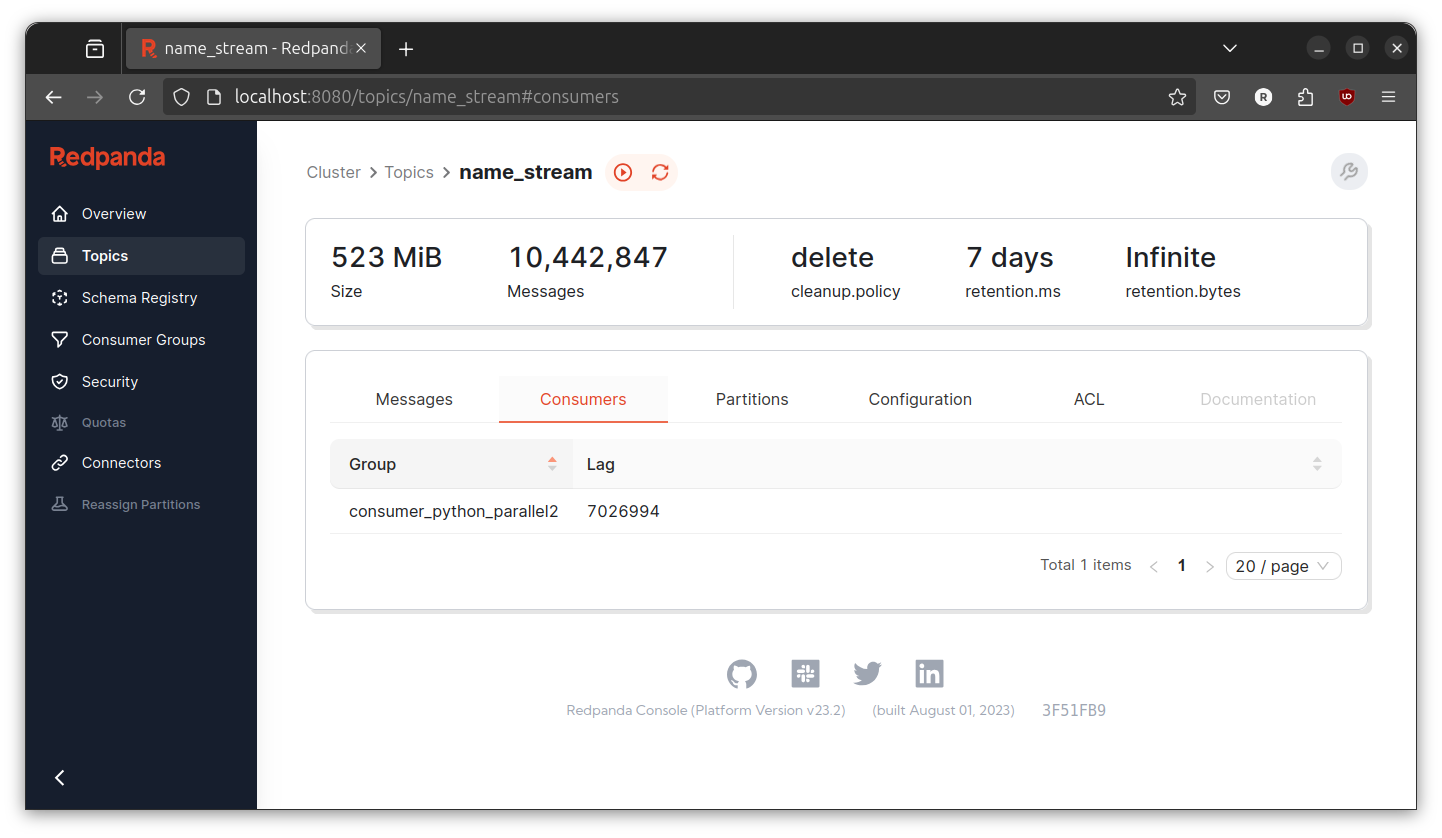
Inspecting the number of consumer lag I can see that the number still increasing. Lets try scale the number of process for (I think) the most heavy part, the hasher.
Create new global variable to keep the number of hasher process. Then update the signaling and process creation. Here is the diff:
--- <unnamed>
+++ <unnamed>
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@
group_id = "consumer_python_parallel2"
broker = "localhost:19092"
queue_limit = 1000 * 1000
+hasher_process_num = 2
class Switch():
is_active = True
@@ -44,7 +45,7 @@
logging.info("consumer receiving signal")
consumer.close()
- q.put(signal.SIGINT)
+ [q.put(signal.SIGINT) for _ in range(hasher_process_num)]
def hasher(consumer_q, producer_q):
@@ -77,14 +78,14 @@
'queue.buffering.max.messages': queue_limit}
producer = Producer(conf)
- while True:
+ signal_count = 0
+ while signal_count != hasher_process_num:
logging.info("producer poll")
item = producer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("producer receiving signal")
- unflushed = producer.flush()
- logging.info(f"unflushed: {unflushed}")
- break
+ signal_count += 1
+ continue
# producer
try:
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
@@ -92,7 +93,8 @@
producer.flush()
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
- producer.flush()
+ unflushed = producer.flush()
+ logging.info(f"unflushed: {unflushed}")
def main():
@@ -101,21 +103,19 @@
producer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
consumer_process = mp.Process(target=consumer, args=(consumer_q,s,))
- hasher_process = mp.Process(target=hasher, args=(consumer_q, producer_q,))
+ hasher_processes = [mp.Process(target=hasher, args=(consumer_q, producer_q,)) for _ in range(hasher_process_num)]
producer_process = mp.Process(target=producer, args=(producer_q,))
-
consumer_process.start()
- hasher_process.start()
+ [hasher_process.start() for hasher_process in hasher_processes]
producer_process.start()
-
consumer_process.join()
- hasher_process.join()
+ [hasher_process.join() for hasher_process in hasher_processes]
producer_process.join()
consumer_process.close()
- hasher_process.close()
+ [hasher_process.close() for hasher_process in hasher_processes]
producer_process.close()
logging.info('all done')
Here is the full code:
from confluent_kafka import Consumer, Producer
from confluent_kafka.error import KafkaError
import hashlib
import json
import sys
import logging
import multiprocessing as mp
import signal
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
topic = 'name_stream'
destination_topic = 'name_stream_parallel2_transformed'
group_id = "consumer_python_parallel2"
broker = "localhost:19092"
queue_limit = 1000 * 1000
hasher_process_num = 2
class Switch():
is_active = True
def __init__(self):
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, self.turn_off)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, self.turn_off)
def turn_off(self, *_):
self.is_active = False
def consumer(q, switch):
logging.info("consumer started")
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'group.id': group_id}
consumer = Consumer(conf)
consumer.subscribe([topic])
while switch.is_active:
msg = consumer.poll(1)
if msg is None: continue
if msg.error():
if msg.error().code() == KafkaError._PARTITION_EOF:
sys.stderr.write('%% %s [%d] reached end at offset %d\n' % (msg.topic(), msg.partition(), msg.offset()))
elif msg.error(): logging.error(msg.error())
else:
q.put((msg.key(), msg.value()))
logging.info("consumer receiving signal")
consumer.close()
[q.put(signal.SIGINT) for _ in range(hasher_process_num)]
def hasher(consumer_q, producer_q):
logging.info('hasher started')
while True:
# tranformation
logging.info("hasher poll")
item = consumer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("hasher receiving signal")
producer_q.put(signal.SIGINT)
return
key = item[0]
value = json.loads(item[1])
value['hash'] = hashlib.md5(item[1]).hexdigest()
producer_q.put((key, value))
def ack(err, msg):
if err is not None:
logging.info("Failed to deliver message: %s: %s" % (str(msg), str(err)))
else:
logging.info("Successfully produced message {} into {}[{}]@{} ".format(str(msg.value()), str(msg.topic()), str(msg.partition()), str(msg.offset())))
def producer(producer_q):
logging.info("producer started")
conf = {'bootstrap.servers': broker,
'queue.buffering.max.messages': queue_limit}
producer = Producer(conf)
signal_count = 0
while signal_count != hasher_process_num:
logging.info("producer poll")
item = producer_q.get()
if item == signal.SIGINT:
logging.info("producer receiving signal")
signal_count += 1
continue
# producer
try:
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
except BufferError:
producer.flush()
producer.produce(destination_topic, key=item[0], value=json.dumps(item[1]), callback=ack)
unflushed = producer.flush()
logging.info(f"unflushed: {unflushed}")
def main():
s = Switch()
consumer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
producer_q = mp.Queue(queue_limit)
consumer_process = mp.Process(target=consumer, args=(consumer_q,s,))
hasher_processes = [mp.Process(target=hasher, args=(consumer_q, producer_q,)) for _ in range(hasher_process_num)]
producer_process = mp.Process(target=producer, args=(producer_q,))
consumer_process.start()
[hasher_process.start() for hasher_process in hasher_processes]
producer_process.start()
consumer_process.join()
[hasher_process.join() for hasher_process in hasher_processes]
producer_process.join()
consumer_process.close()
[hasher_process.close() for hasher_process in hasher_processes]
producer_process.close()
logging.info('all done')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
Delete all the left over topics and run again.
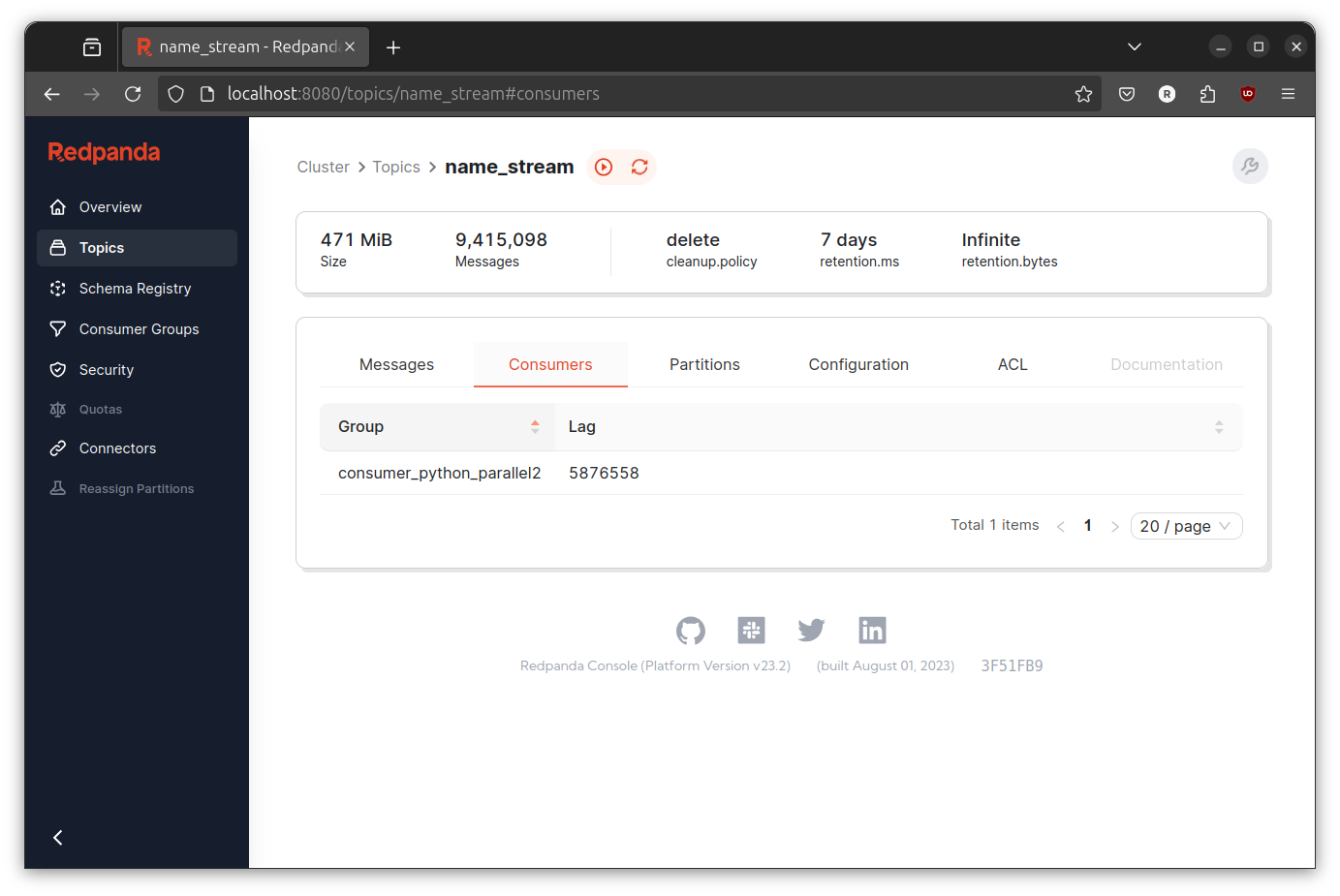
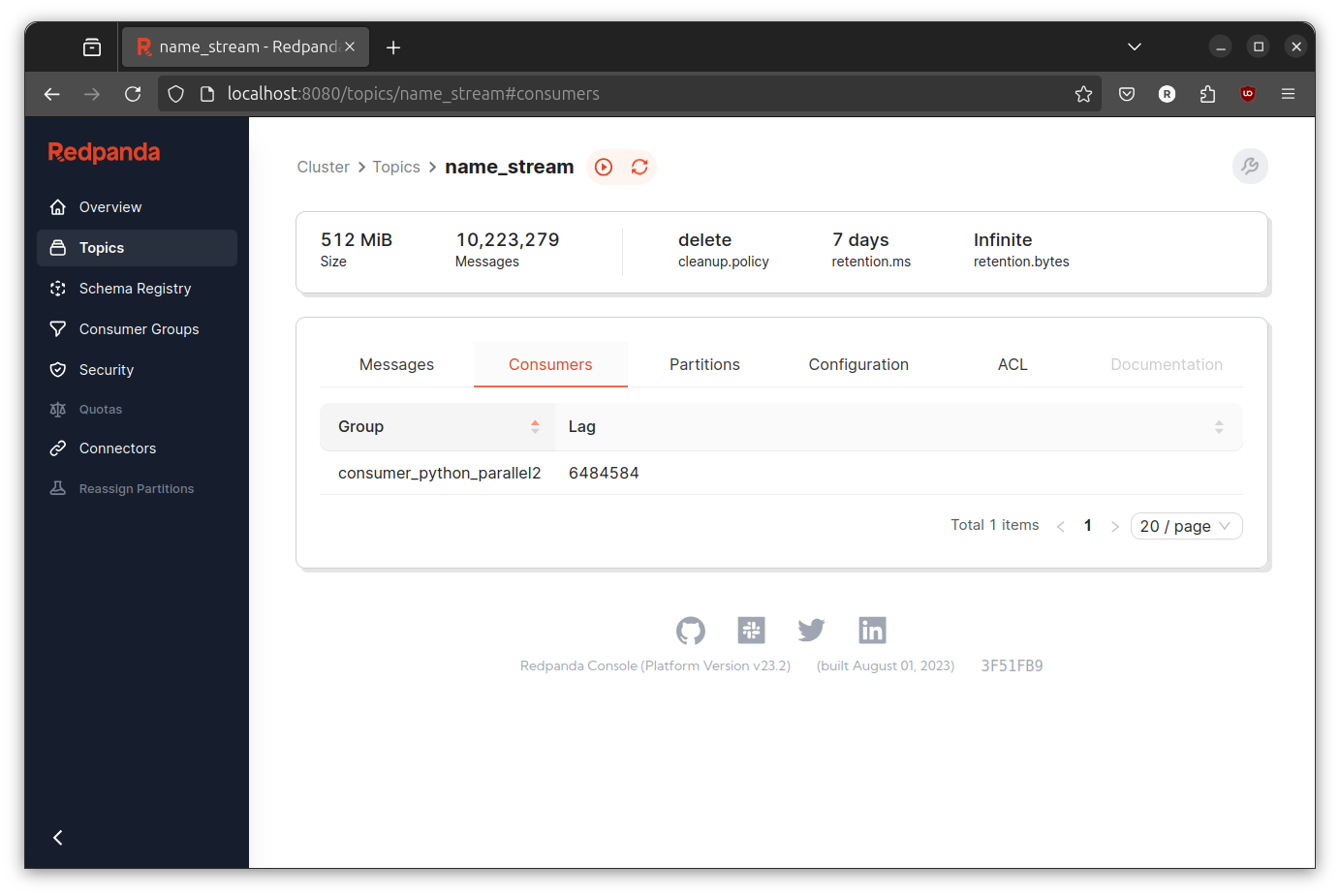
Same stories! Consumer lag still increasing, though not really rapidly like before. To be completely honest, I start too doubt myself. I clearly remember that pipelining is enough for this case (I have implemented this in the past). However, even after scale the number of hasher the consumer lag still increasing.
While trying to find the bottleneck (and getting annoyed by logging flood in the process) I remember someone ever said that “writing to stdout is expensive”. Maybe the logging is too verbose? Lets try changing the logging level.
Here is the diff:
--- <unnamed>
+++ <unnamed>
@@ -7,7 +7,7 @@
import multiprocessing as mp
import signal
-logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
+logging.basicConfig(level=logging.CRITICAL)
topic = 'name_stream'
destination_topic = 'name_stream_parallel2_transformed'
group_id = "consumer_python_parallel2"
Clean up the topic and run again.
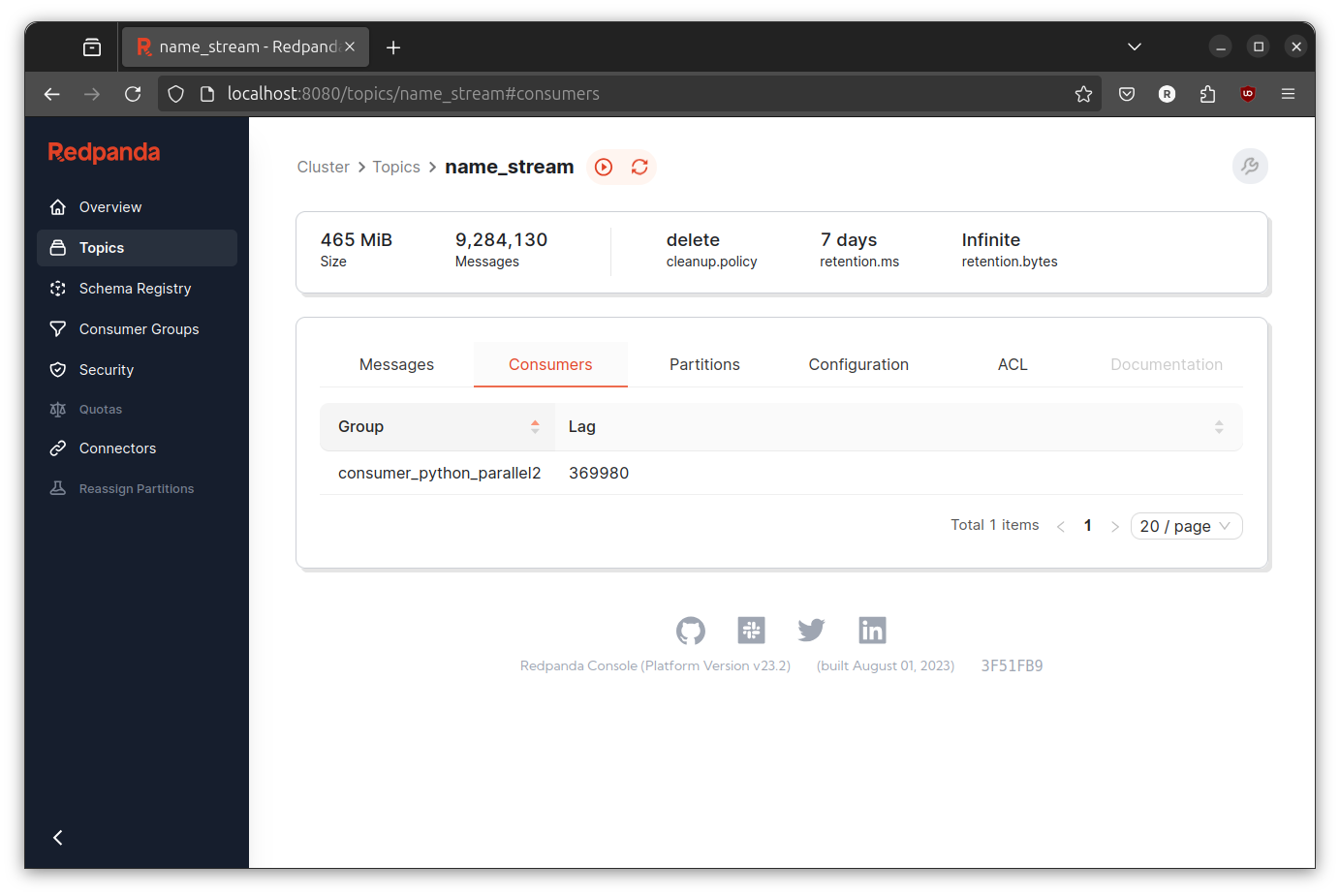
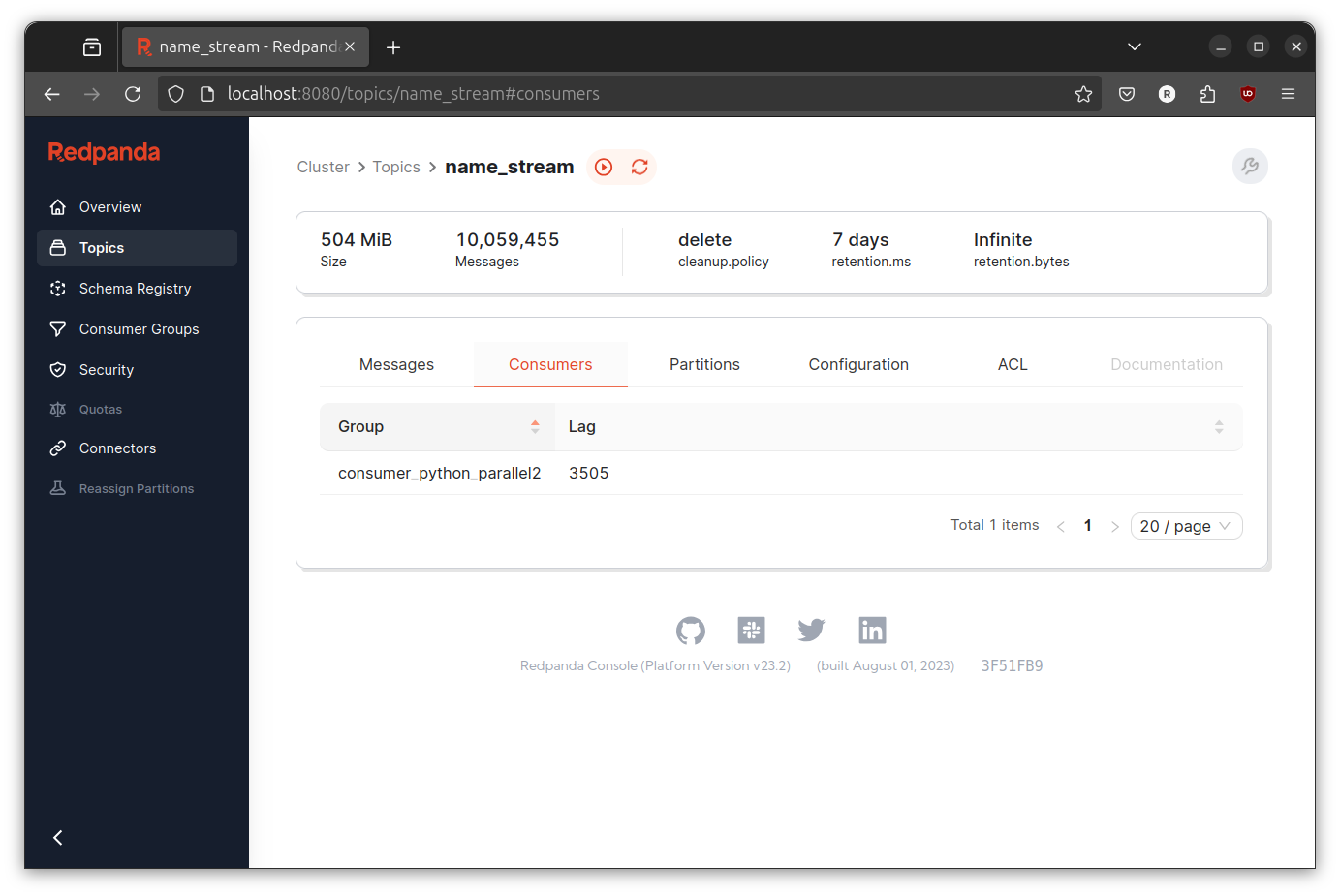
IT IS WORKING! The throughput is indeed better than before.
If you compare the screenshot from the serial implementation and the last implementation, you can clearly see that the troughput is definitely better. Although if you run it multiple times, you will see that the transformer most of the time cannot keep up with the production rate. However, I think we already achieve our initial goal and I will consider it done (at least for now).
You can find all the code at https://github.com/rochimfn/resource-python-transformer-multiprocessing. There are a lot of homework until the code is considered done. The error handling is not proper. There is no retry when some step fail. The autocommit. Even the the Dead Letter Queue is not present. Anyway, thanks for reading and see you next time.