Frappe Development Environment on LXD Container
Frappe is low code web framework written in Python and JS. Frappe the building block of ERPNext, popular open source ERP software. Since you are here, I guess you already know frappe. Learn more about frappe at https://frappe.io/framework.
LXD is open source container and virtualization solution from Canonical. LXD support both container and virtual machine. Unlike docker that focused on application containerization, LXD focused on system containerization. From user perspective, operating LXD container is like operating virtual machine but with less resource usage. LXD also support clustering, this feature is very handy if you need high availability, load balance, or spawn a lot of instance. Learn more about LXD at https://canonical.com/lxd.
Prepare The LXD
The easiest way to install LXD is through snap and on Ubuntu OS.
Install LXD:
sudo snap install lxd
Add current user to lxd group:
getent group lxd | grep -qwF "$USER" || sudo usermod -aG lxd "$USER"
Restart!
Initiate LXD, just hit enter to pick the default value:
lxd init
You can read more about LXD installation here. You can enable the web ui by following the docs here.
Setup Bench
Run below command to create new Ubuntu 24.04 container:
lxc launch ubuntu:24.04 frappe-development-machine -c limits.cpu=2 -c limits.memory=4GiB -d root,size=30GiB
Argument config (-c) and device (-d) is not mandatory.
Check the state of the newly created container:
lxc list --fast
The frappe-development-machine should be RUNNING.
Enter the container:
lxc shell frappe-development-machine
Update the system:
apt update && apt upgrade -y
Install prerequisities for frappe bench:
apt install git python-is-python3 python3-dev python3-pip python3.12-venv redis-server mariadb-server xvfb libfontconfig wkhtmltopdf
Configure the mariadb server. Other than new root password, the default value is fine:
mariadb-secure-installation
Create new mariadb configuration to set the encoding:
vim /etc/mysql/mariadb.conf.d/99-frappe.cnf
Insert below configuration:
[mysqld]
character-set-client-handshake = FALSE
character-set-server = utf8mb4
collation-server = utf8mb4_unicode_ci
[mysql]
default-character-set = utf8mb4
Restart mariadb-server:
systemctl restart mariadb
Check the flag:
mariadbd --print-defaults
The configuration in 99-frappe.cnf file should be reflected as flag for mariadbd.
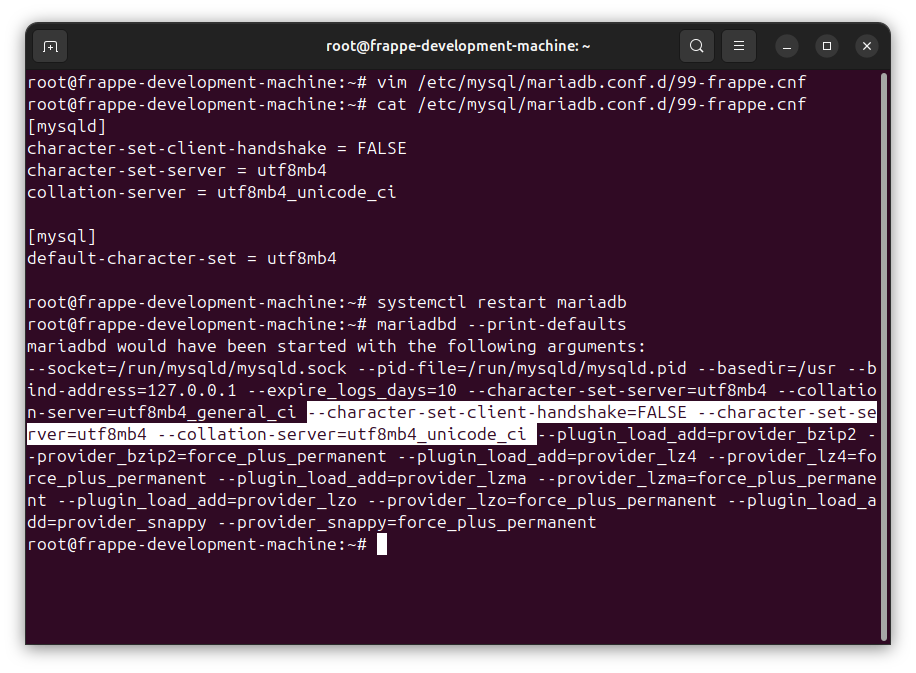
Don’t worry about duplicate flag. “If an option is set multiple times, the later setting will override the earlier setting/s”, from mariadb documentation.
Login as user ubuntu:
su - ubuntu
Install node and yarn. I am very familiar with volta, so I will use it:
curl https://get.volta.sh | bash
. .bashrc
volta install node@lts
volta install yarn@1
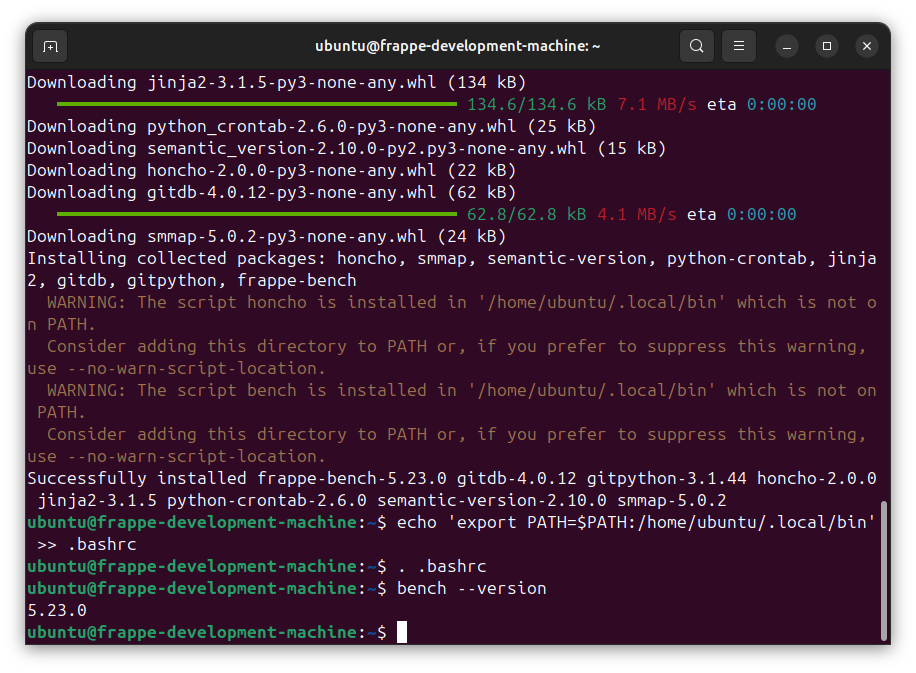
Install bench:
pip install frappe-bench --break-system-packages
echo 'export PATH=$PATH:/home/ubuntu/.local/bin' >> .bashrc
. .bashrc
bench --version
Init frappe project:
cd
bench init frappe-bench
Init frappe sites and apps:
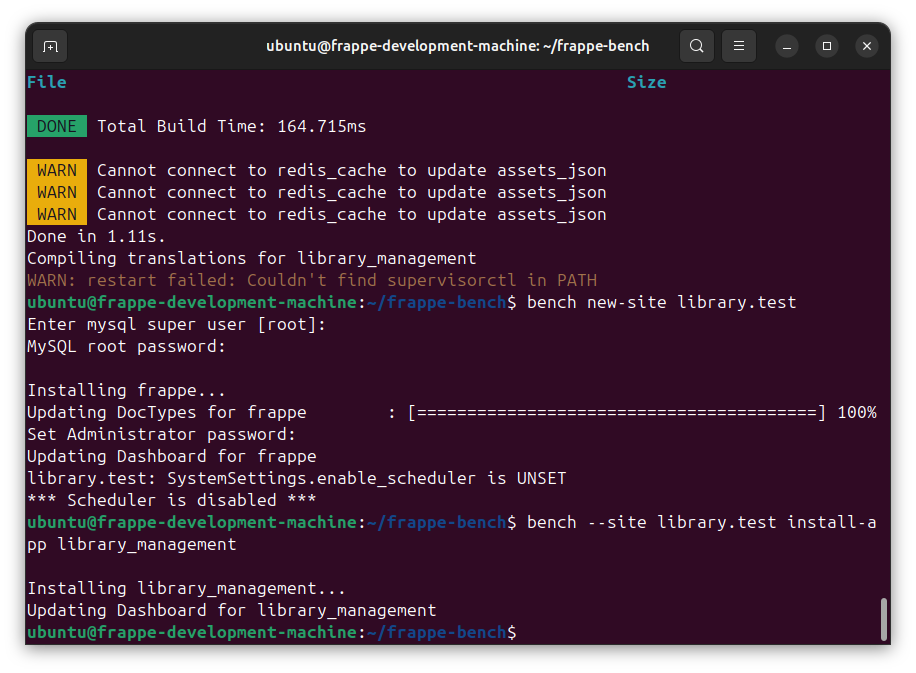
cd frappe-bench
bench new-app library_management
bench new-site library.test
bench --site library.test install-app library_management
Setup SSH
Setup SSH to make the container accessible like remote machine.
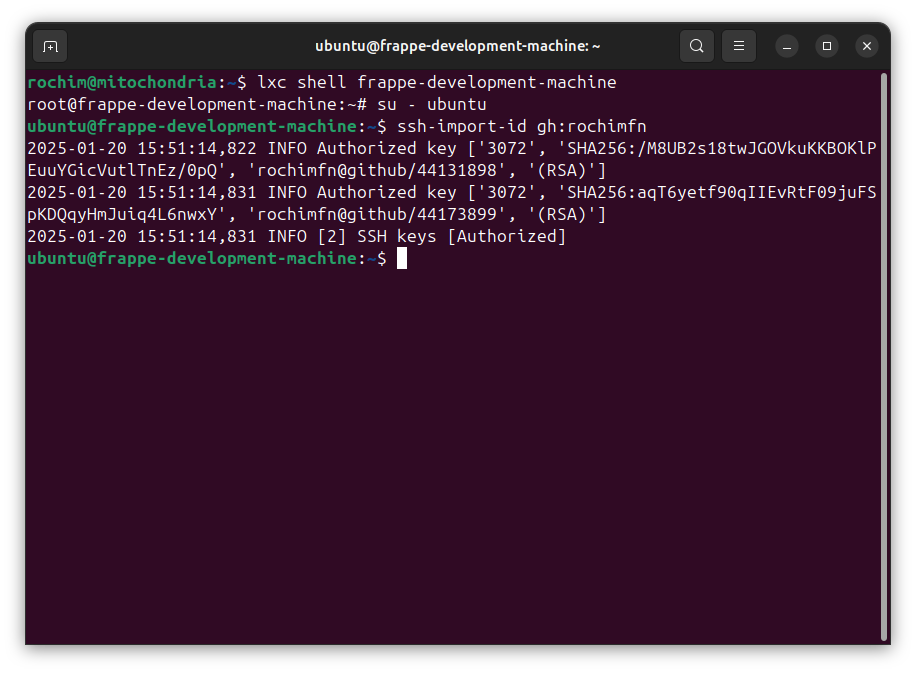
Enter the container as user ubuntu:
lxc shell frappe-development-machine
su - ubuntu
My public keys is on github, so I can easily imported it using ssh-import-id:
ssh-import-id gh:rochimfn
Or manually configure .ssh/authorized_keys file:
mkdir -p .ssh
chmod 700 .ssh
vim .ssh/authorized_keys # <- copy your public keys here
chmod 600 .ssh/authorized_keys
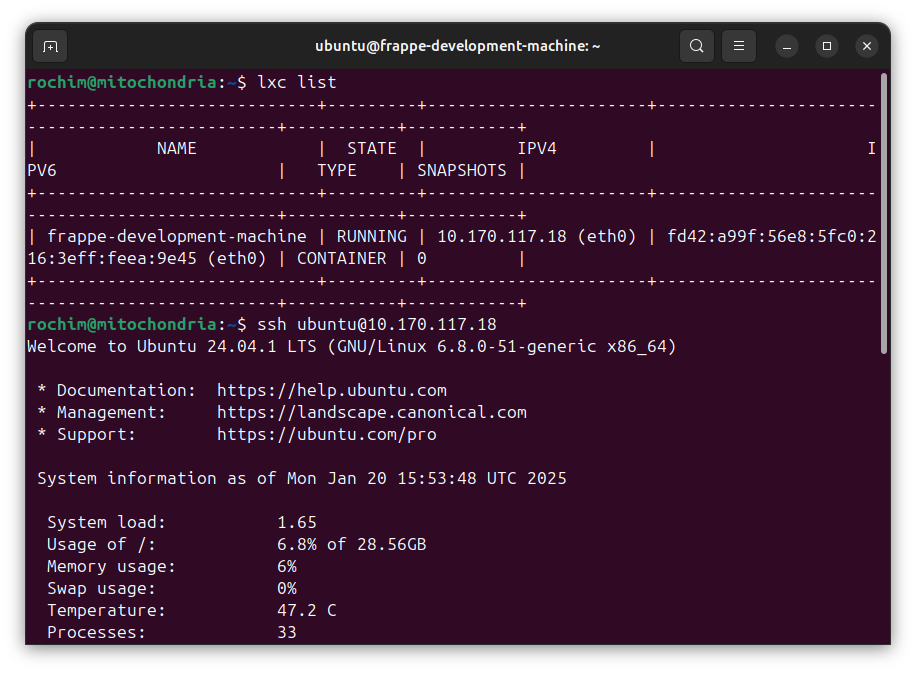
Open another terminal. Find the ip of the container:
lxc list
SSH into the container:
ssh ubuntu@10.170.117.18
# or
ssh ubuntu@10.170.117.18 -i .ssh/id_ed25519 # change with name of your private keys
Access The Web Server
Write the ip of the containner:
lxc list
Add new record to the host /etc/host:
sudo vim /etc/host
Fill with the hostname of the frappe app and ip of the container:
10.170.117.18 library.test
Start the bench from container (via ssh or lxc shell as user ubuntu):
cd frappe-bench
bench start
Open http://library.test:8000 with web browser.
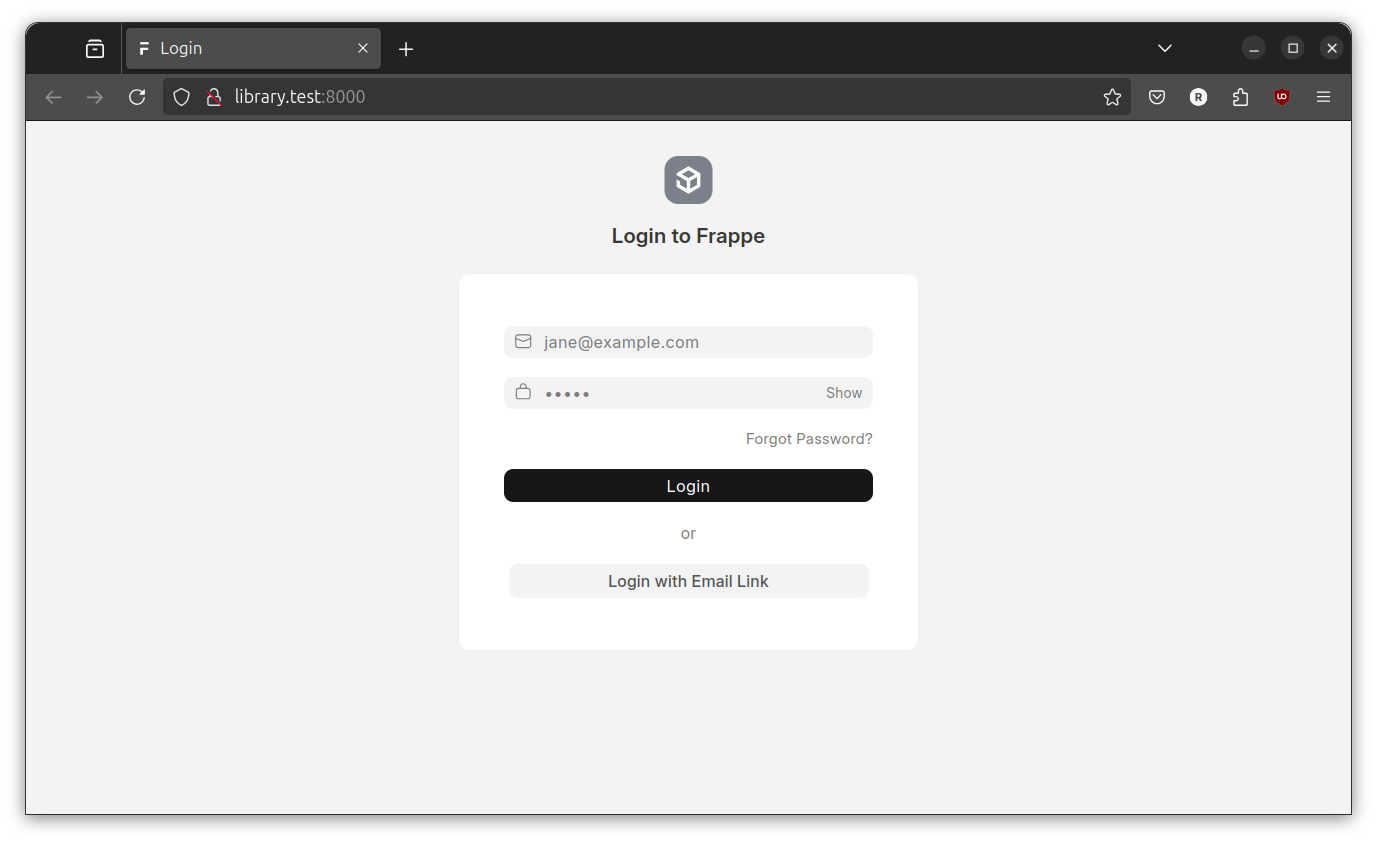
Connect with Visual Studio Code
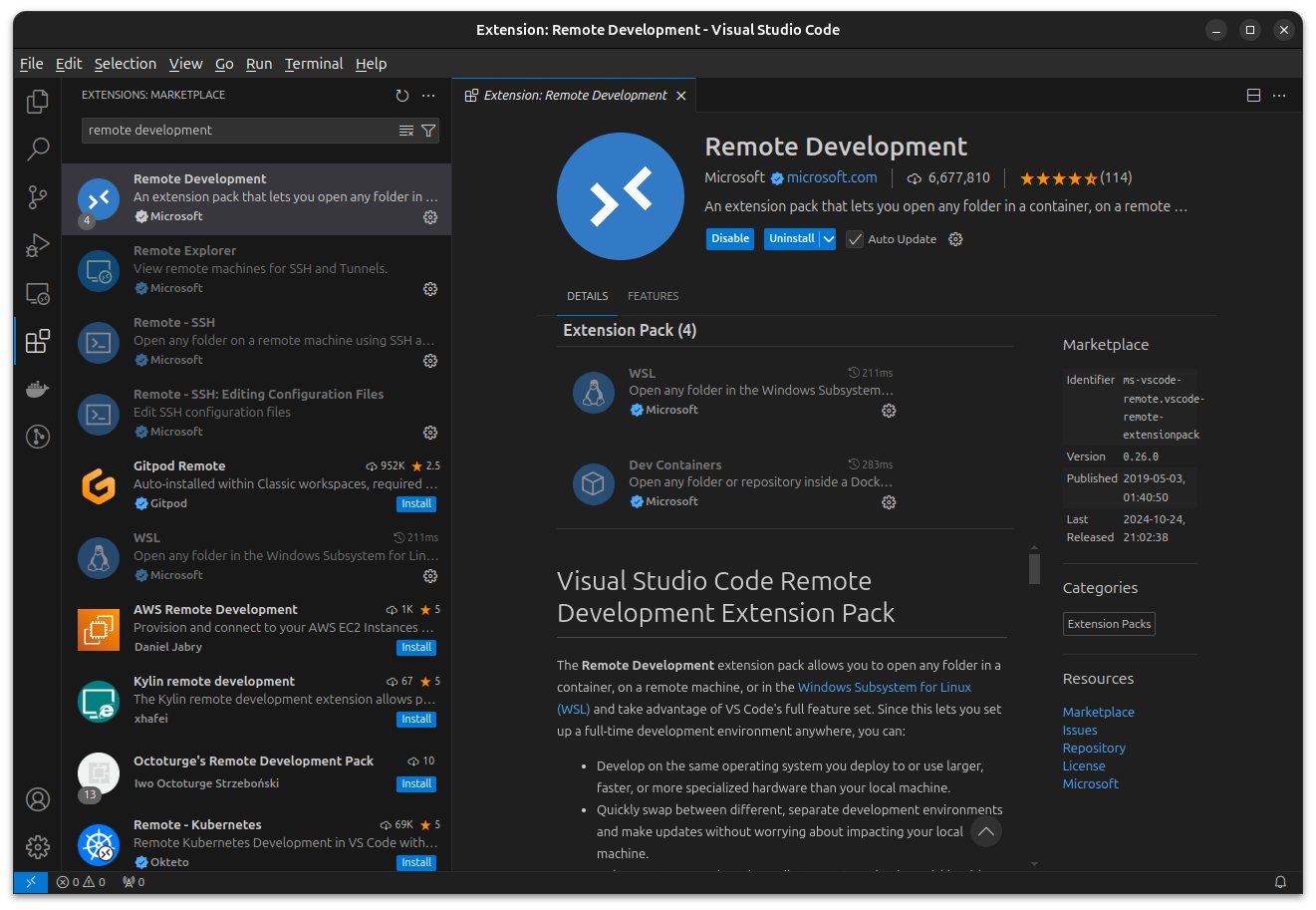
Install Remote Development extensions from Visual Studio Code Extensions Marketplace.
Create ssh config file on host machine:
touch .ssh/config
chmod 664 .ssh/config
vim .ssh/config
Register the container ssh config:
Host frappe-development-machine
HostName 10.170.117.18
User ubuntu
Port 22
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_ed25519
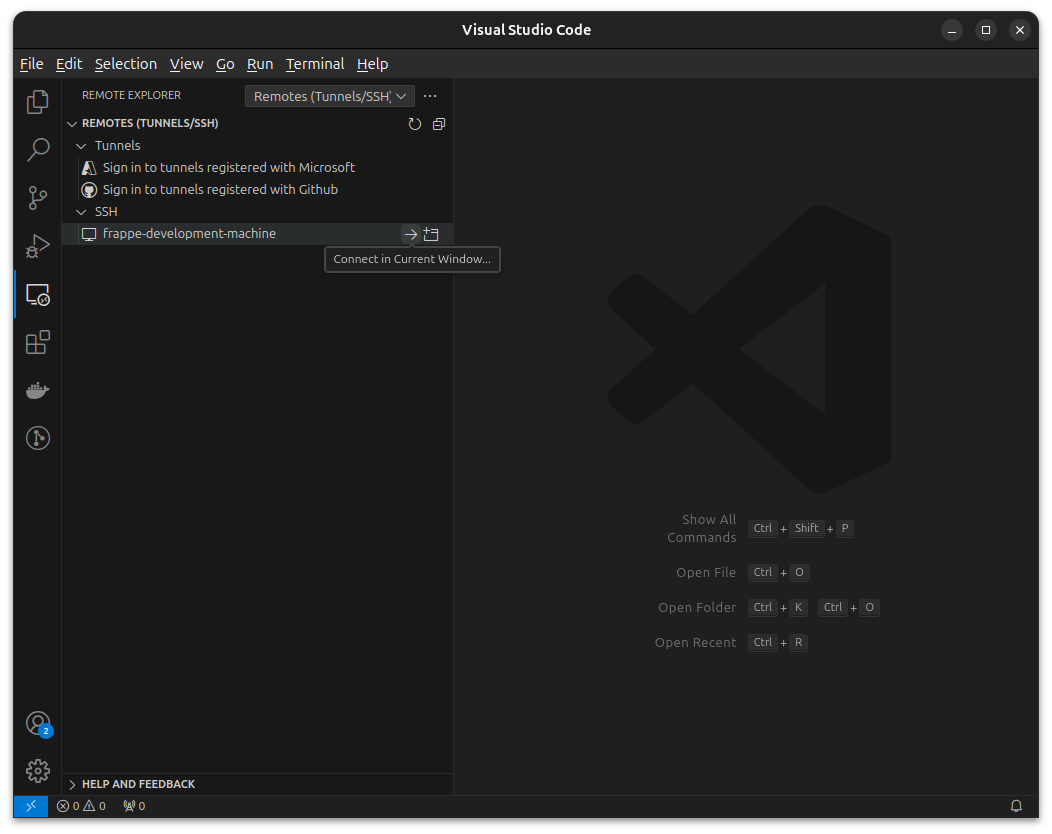
Open the Remote Development menu from sidebar and the frappe-development-machine will be there. Click on Connect in Current Window… or Connect in New Window…. Then Open Folder and choose the bench directory.
Why use LXD?
I don’t know. But, LXD container is … container. This means the whole environment is isolated, so I don’t have to worry the libraries, python version, and other component conflicting with another project on my host. LXD container behave like virtual machine, I find it easier to deal with vs development inside docker/dev container (of course its difference story for deployment). Also container resource usage is shared and minimal (vs virtual machine). Last but not least, LXD support clustering.